Greatwall Kinase Inhibition
Developing selective chemical inhibitors to study mitotic regulation and explore therapeutic applications.
Live imaging of cells treated with Greatwall inhibitor showing cytokinetic failure
Research Overview: Targeting the Guardian of Mitosis
Greatwall kinase (MASTL) acts as a critical guardian during cell division, ensuring that once mitosis begins, cells complete the process correctly. It works by suppressing PP2A-B55α phosphatase activity, preventing premature reversal of the mitotic state. We developed selective chemical inhibitors to understand this process and explore whether disrupting this guardian could be therapeutically useful.
C-604: A Tool Compound for Studying Mitosis
In collaboration with the Sussex Drug Discovery Centre and AstraZeneca, we developed C-604 (also known as UOS-00054604), a highly selective Greatwall inhibitor with sub-micromolar potency. This compound has proven invaluable for dissecting the molecular mechanisms of mitotic regulation.
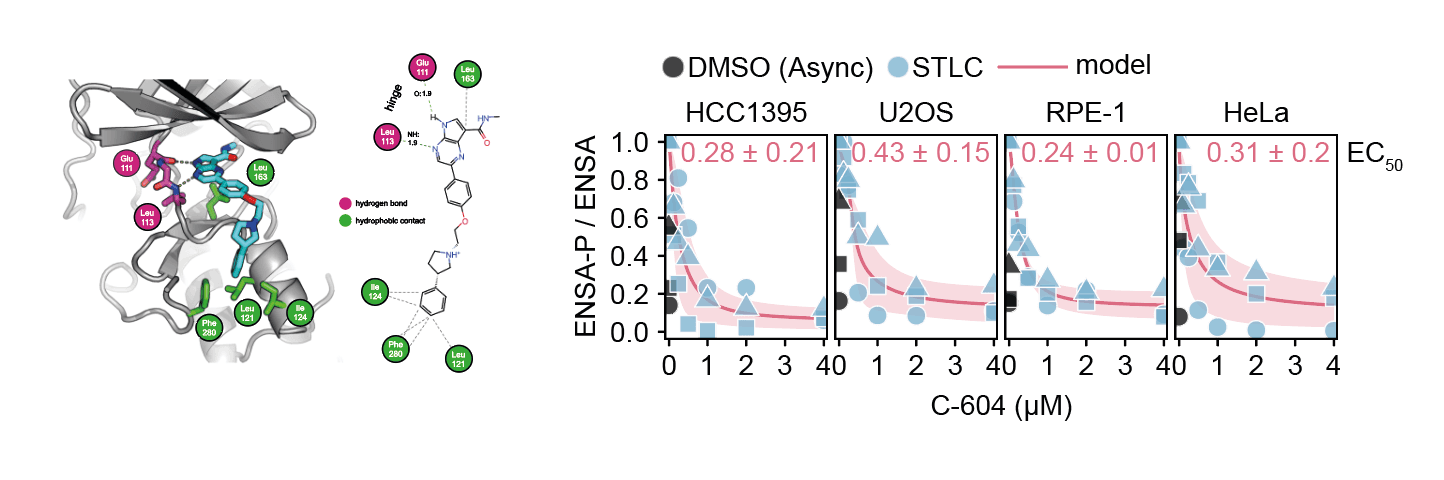
Using C-604, we discovered that Greatwall inhibition leads primarily to cytokinetic failure — cells attempt to divide but fail to properly separate, resulting in multinucleated cells. This phenotype is entirely dependent on PP2A-B55α phosphatase activity, confirming the specific pathway through which Greatwall maintains mitotic fidelity.
A Predictive Biomarker for Sensitivity
Perhaps our most significant finding was identifying the B55α-to-Greatwall expression ratio as a powerful predictor of cellular sensitivity to Greatwall inhibition. Cancer cell lines with high B55α and low Greatwall expression are particularly vulnerable to these inhibitors, while the reverse pattern confers resistance.
This protein expression ratio can predict sensitivity with remarkable accuracy (R² = 0.81), providing a potential companion diagnostic for therapeutic applications. Clinical candidates derived from this project have been licensed and are currently being evaluated in Phase I trials.
Key Research Findings
- • Development of C-604, a selective Greatwall inhibitor
- • Cytokinetic failure as primary phenotype
- • PP2A-B55α-specific mechanism of action
- • B55α/Greatwall ratio as predictive biomarker
- • Phosphoproteome analysis during inhibition
Collaborations & Funding
This work was conducted as part of a Wellcome Trust Portfolio Award, in collaboration with:
- • Sussex Drug Discovery Centre
- • AstraZeneca
Current research is supported by a Cancer Research UK Programme Grant.
From Discovery to Clinical Development
Tool Compound Development
C-604 was identified through screening approximately 40,000 compounds, with outstanding kinome selectivity and minimal off-target effects. It remains a valuable research tool for studying mitotic regulation.
Mechanistic Understanding
Our phosphoproteomic studies revealed that C-604 destabilizes the mitotic phosphoproteome, affecting hundreds of phosphorylation sites primarily on CDK1 substrates, exclusively through PP2A-B55α activation.
Clinical Translation
Building on insights from C-604, optimized clinical candidates have been licensed and entered Phase I trials, with the B55α/Greatwall expression ratio serving as a potential companion diagnostic.